1. Electrolytes and non-electrolytes
Electrolytes - water solutions and melted salts, capable of conducting electricity.
Non-electrolytes - water solutions unable to conduct electricity
Indicators - substances which change their colors in the presence of acids and/or bases
2. Acids
Acids are chemical compounds which consist of at least 1 hydrogen atom and only 1 acid remain.
Their general formula is HnR where:
H - hydrogen atom
n - number of hydrogen atoms
R - acid remain
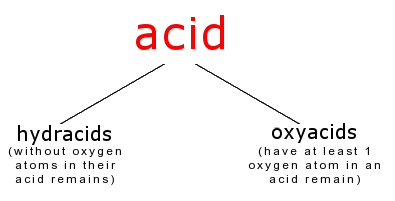
Hydracids
HCl - hydrochloric acid (strong)
HBr - hydrobromic acid (strong)
HI - hydroionic acid (strong)
HF - hydrofluoric acid (weak)
H₂S - hydrosulphuric acid (weak)
Oxyacids
H₂SO₄ - sulphuric acid(strong)
H₂SO₃ - sulphuric acid (weak)
HNO₃ - nitric (V) acid (strong)
HNO₂ - nitric (III) acid (weak)
H₂CO₃ - carbonic acid (weak)
H₃PO₄ - phosphoric (V) acid/orthophosphoric acid
H₃BO₃ - boric acid/boronic acid
denaturation - a structural change in macromolecules caused by extreme conditions
hygroscopic - an ability of a substance to attract and hold water molecules from the surrounding environment
carbonisation - the term for the conversion of an organic substance into carbon or a carbon-containing residue
residue - pozostałość
corrosive - żrący
rotten - zgniły
cancerogenic - rakotwórczy
impermanent - niestały
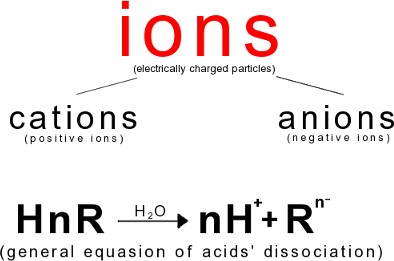
3. Ionic dissociation
Dissociation is a decomposition of molecules into ions.
4. Hydroxides and bases
Hydroxides are compounds which consist of only 1 atom and at least 1hydroxylic group.
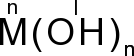
M - a metal atom
OH - a hydroxylic group
n - number of hydroxylic groups = valency of a metal
Bases are water solutions of hydroxides.
NaOH - sodium hydroxide/sodium base
KOH - potasium hydroxide/potasium base
CA(OH)₂ - calcium hydroxide/calcium base
MG(OH)₂ - magnesium hydroxide
Cu(OH)₂ - cooper(II) hydroxide
Fe(OH)₂ - ironium(V) hydroxide
Fe(OH)₃ - ironium(VI) hydroxide
Al(OH)₃ - to je amelinium, tego nie pomalujesz!
NH₄OH(NH₃ H₂O) - ammonia base
H₂O) - ammonia base
Features of sodium hydroxides: solid, white, soapy taste, soliable in water, hygroscopic, corrosive
Features of sodium base: liquid, colourless, soapy taste, water soliable, corrosive
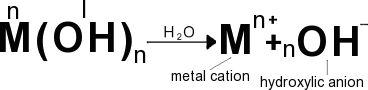
Dissocciation of bases
5. Reaction of solution and pH
acidic reaction: a number of hydrogen cations is greater than a number of hydrogen anions there
[H⁺] > [OH⁻]
basic (alkaline) reaction: a number of hydroxylic is greater than a number of hydrogen cations there
[OH⁻] > [H⁺]
neutral reaction: numbers of hydrogen cations and hydroxylic anions are equal there
[H⁺] = [OH⁻]
reaction - odczyn
acetic acid - kwas octowy
Electrolytes - water solutions and melted salts, capable of conducting electricity.
Non-electrolytes - water solutions unable to conduct electricity
Indicators - substances which change their colors in the presence of acids and/or bases
| neutral (water) | acidic | basic (alkaline) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| universal indicator | yellow | red | blue |
| litmus | pink | red | blue |
| phenolophtaleine | colorless | colorless | rasp red |
| methyl orange | orange | red | yellow |
| tea essence | brown | straw yellow | brown |
| red cabbage decoction | purple/pale blue | red | green |
2. Acids
Acids are chemical compounds which consist of at least 1 hydrogen atom and only 1 acid remain.
Their general formula is HnR where:
H - hydrogen atom
n - number of hydrogen atoms
R - acid remain

Hydracids
HCl - hydrochloric acid (strong)
HBr - hydrobromic acid (strong)
HI - hydroionic acid (strong)
HF - hydrofluoric acid (weak)
H₂S - hydrosulphuric acid (weak)
Oxyacids
H₂SO₄ - sulphuric acid(strong)
H₂SO₃ - sulphuric acid (weak)
HNO₃ - nitric (V) acid (strong)
HNO₂ - nitric (III) acid (weak)
H₂CO₃ - carbonic acid (weak)
H₃PO₄ - phosphoric (V) acid/orthophosphoric acid
H₃BO₃ - boric acid/boronic acid
| phase | color | taste | solubility in water | odour | other features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCl | liquid | colorless | sour | yes | choking | |
| H₂S | liquid | yellowish | sour | yes | rotten eggs | |
| H₂SO₄ | liquid | colorless | sour | yes | odourless | |
| HNO₃ | liquid | colorless | sour | yes | choking | causes protein degeneration |
| H₃PO₄ | solid | colorless | sour | yes | odourless | |
| H₃BO₃ | solid | colorless | slightly sour | yes | odourless | |
| H₂CO₃ | liquid | colorless | sour | yes | odourless | extremely impermanent |
denaturation - a structural change in macromolecules caused by extreme conditions
hygroscopic - an ability of a substance to attract and hold water molecules from the surrounding environment
carbonisation - the term for the conversion of an organic substance into carbon or a carbon-containing residue
residue - pozostałość
corrosive - żrący
rotten - zgniły
cancerogenic - rakotwórczy
impermanent - niestały
3. Ionic dissociation
Dissociation is a decomposition of molecules into ions.

4. Hydroxides and bases
Hydroxides are compounds which consist of only 1 atom and at least 1hydroxylic group.
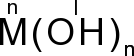
M - a metal atom
OH - a hydroxylic group
n - number of hydroxylic groups = valency of a metal
Bases are water solutions of hydroxides.
NaOH - sodium hydroxide/sodium base
KOH - potasium hydroxide/potasium base
CA(OH)₂ - calcium hydroxide/calcium base
MG(OH)₂ - magnesium hydroxide
Cu(OH)₂ - cooper(II) hydroxide
Fe(OH)₂ - ironium(V) hydroxide
Fe(OH)₃ - ironium(VI) hydroxide
Al(OH)₃ - to je amelinium, tego nie pomalujesz!
NH₄OH(NH₃
 H₂O) - ammonia base
H₂O) - ammonia baseFeatures of sodium hydroxides: solid, white, soapy taste, soliable in water, hygroscopic, corrosive
Features of sodium base: liquid, colourless, soapy taste, water soliable, corrosive
Dissocciation of bases

5. Reaction of solution and pH
acidic reaction: a number of hydrogen cations is greater than a number of hydrogen anions there
[H⁺] > [OH⁻]
basic (alkaline) reaction: a number of hydroxylic is greater than a number of hydrogen cations there
[OH⁻] > [H⁺]
neutral reaction: numbers of hydrogen cations and hydroxylic anions are equal there
[H⁺] = [OH⁻]
reaction - odczyn
acetic acid - kwas octowy
©2011-2013 by Oskar Zmarzły
