1. Atomic structure
- There are protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons move around electron shells
Atom - the smallest indivisible part of an element which keeps every feature of it; consists of a nucleus and electron shells
Proton - the elementary particle with a positive charge
Neutron - the elementary particle without charge
- A number of protons and a number of electrons is equal in a particular elements; and that's why atom is electrically neutral
Electron configuration - arrangement of electrons on shells
2. Isotopes
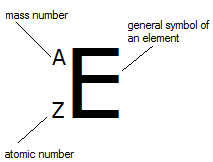
Z (atomic number) - number of protons inside a nucleus a particular atom. Number of electrons is the same as the number of protons.
A (mass number) - sum of numbers of protons and neutrons in nucleus
A - Z = number of neutrons
Isotopes - atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass number. It means they have the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.
Radioactivity - an ability of some nuclei to emit radiation
Natural radioactivity - an ability to radiate itself (no human action)
Artifical radioactivity - if a nucleus is incapable to radiate; a human action can induce it by some reactions
3. The periodic table of elements
- The periodic table is built of 18 groups (vertical rows) and 7 periods (horizontal rows).
- Groups 1, 2, 13-18 are main groups
- Groups 3-12 are additional groups
Information we can get from a number of group:
- A number of valence:
- for groups 1 and 2 it's equal to number of group
- for groups 13-18 it's equal to number of group -10
- Valency: - for groups 1, 2 it's equal to number of group
- for groups 13-18 is equal to number of group -10
Information we can get from a number of period:
- Number of electron shells
- Every group's name comes from the name of the first element
- Exception is the first group, which name is lithium family
- 17th group can be called: fluorine family, chlorine family, halogens
- 18th group can be called: noble gases, helium family
lantanowce - lanthanides
aktynowce - actanides
4. Types of bondings
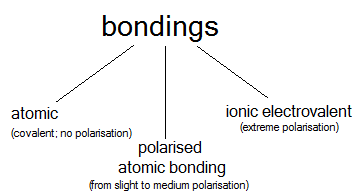
- A bonding is a pair of electrons; every electron comes from a different atom. Only valence electrons are able to form bondings
- As a result of bonding formation molecules are obtained
- Atomic bonding is always formed only between 2 non-metal atoms
- The most often bonding are formed are called homoatomic molecules; the exception is C-H bonding
- Homoatomic molecule consists of atoms of the same element.
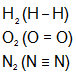
- An electron pair is used equally by both atoms

- There are protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons move around electron shells
Atom - the smallest indivisible part of an element which keeps every feature of it; consists of a nucleus and electron shells
Proton - the elementary particle with a positive charge
Neutron - the elementary particle without charge
- A number of protons and a number of electrons is equal in a particular elements; and that's why atom is electrically neutral
Electron configuration - arrangement of electrons on shells
2. Isotopes

Z (atomic number) - number of protons inside a nucleus a particular atom. Number of electrons is the same as the number of protons.
A (mass number) - sum of numbers of protons and neutrons in nucleus
A - Z = number of neutrons
Isotopes - atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass number. It means they have the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.
| . | Particules/Isotope | Number of protons | Number of electrons | Number of neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protium | 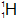 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Deuterium | 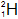 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tritium | 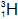 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Radioactivity - an ability of some nuclei to emit radiation
Natural radioactivity - an ability to radiate itself (no human action)
Artifical radioactivity - if a nucleus is incapable to radiate; a human action can induce it by some reactions
3. The periodic table of elements
- The periodic table is built of 18 groups (vertical rows) and 7 periods (horizontal rows).
- Groups 1, 2, 13-18 are main groups
- Groups 3-12 are additional groups
Information we can get from a number of group:
- A number of valence:
- for groups 1 and 2 it's equal to number of group
- for groups 13-18 it's equal to number of group -10
- Valency: - for groups 1, 2 it's equal to number of group
- for groups 13-18 is equal to number of group -10
Information we can get from a number of period:
- Number of electron shells
- Every group's name comes from the name of the first element
- Exception is the first group, which name is lithium family
- 17th group can be called: fluorine family, chlorine family, halogens
- 18th group can be called: noble gases, helium family
lantanowce - lanthanides
aktynowce - actanides
4. Types of bondings

- A bonding is a pair of electrons; every electron comes from a different atom. Only valence electrons are able to form bondings
- As a result of bonding formation molecules are obtained
- Atomic bonding is always formed only between 2 non-metal atoms
- The most often bonding are formed are called homoatomic molecules; the exception is C-H bonding
- Homoatomic molecule consists of atoms of the same element.
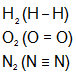
- An electron pair is used equally by both atoms
©2011-2013 by Oskar Zmarzły
Darmowy hosting zapewnia PRV.PL
