Plants
1. General characteristics of plants
- They are autothropic
- They can photosynthesise
- They have got flowers and leaves
- Their cells contain chlorophyll
- They have roots
- They are eucaryotes - their cells have the nucleus
- Their cell wall is made of cellulose
- They have got vacuoles
samożywny - autothropic
eukarioty - eucaryotes
jądro - nucleus
wodniczka - vacuole
2. Plants' reproduction
- Plants have sex organs which prevent of desiccation (drying out) of developing gamets
- Sex organs prevent them by providing them with water and nutrients within a female reproductive structure
- Almost all of them reproduce sexually
- Have a life cycle that is alternation of generations
- Alternation of generations is a term used for describing the life cycle of plants; can exist in two forms: gametophyte and sporophyte
desiccation - wysychanie
developing (gamets) - rozwijające się (gamety)
alternation of generations - przemiana pokoleń
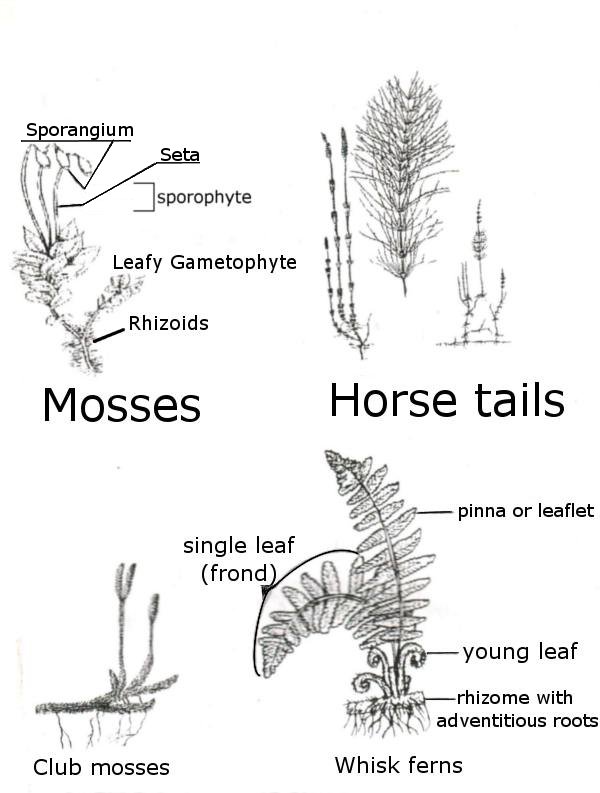
3. Non-vascular plants
- They are restricted to the bryophytes
- Only bryophytes haven't got the vascular tissue for water transport
- Bryophytes include liveworts and mosses
- They can be found in moist locations, because they haven't got roots, leaves and vascular tissue
Reproduction of bryophytes:
- In alternation of generations the gametophyte is dominant
- They need water for fertilization, because the sperm must swim in external moisture to reach the eggs (during sexual reproduction)
a gametophyte - a small, free-living organism that produce gamets (sperm and egg cells); they need water for fertilization
a sporophyte - produces many windblown spores, that disperse the species
rośliny naczyniowe - vascular plants
mszaki - bryophytes
tkanka przewodząca - vascular tissue
wątrobowce - liveworts
mchy - mosses
wilgotne (miejsca) - moist locations
rozprzestrzeniać - to disperse
zapłodnienie - fertilization
4. Primitive vascular plants
- Ferns are primitive vascular plants
- They have true leaves and roots
- They haven't got flowers and seeds, but they reproduce by
spores - Their life cycle (alternation of generations) is characterised by a dominant sporophyte; they produce spores
- Ferns vary in appearance; many of them are low-lying, but there are also tall-tree ferns in the tropics
- Ferns grow in moist and shady woodlands, deserts, rocks, open field, in water
- There are about 10.000 species known - including: whisk ferns, horse tails and club mosses
paprocie - ferns
nizinny - low-lying
zacieniony - shady
paprocie - whisk ferns
skrzypy - horse tails
widłaki - club mosses
korzenie przybyszowe - adventitious roots
5. Seed plants; gymnosperms
- They are vascular plants that produce seeds
- A seed consists of a plant embryo packed along with a food supply within a protective coat
- After a period of dormancy and when environmental factors are favourable (suitable temperature, water and oxygene), stored food will be mobilized and the seed will germinate
- A seed become an important means of dispersing offspring
- A pollen grain can be dispersed through the air or transported by animals - it doesn't need water for fertilizaton
- Seeds-bearing plants are the most succesful land plants, and they dominate the Earth's land-base vegetation
Gymnosperms
- They are group of seed plants with ovules on scales, which are usually arranged in cone-like structures
- Most of them are evergreen (retain leaves throughout the year)
- The needle-shaped leaves are adapted to dry conditions
- Coniferous trees are the oldest and the largest organisms on Earth
nagonasienne - gymnosperms
kiełkować - to germinate
w kształcie igły - needle-shaped
łuska (zalążki na łuskach - scale (ovules on scale)
wiecznie zielone - evergreen
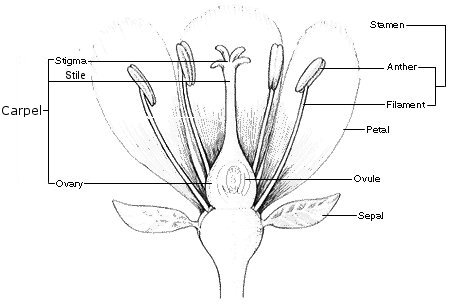
pylnik - anther
pręcik - stamen
nitka pręcika - filament
płatki korony - petals
działki kielicha - sepals
znamię słupka - stigma
szyjka - stile
słupek - carpel
zalążek - ovule
zalążnia - ovary
sosna - pine
świerk - spruce
kosodrzewina - dwarf
limba - swiss pine
jodła - fir
cis - yew
jałowiec - juniper
modrzew - larch
6. Seed plants; angiosperms
- Angiosperms (flowering plants) are vascular seed plants that produce flower and fruits as reproductive structures
- They are most diversed and geographically widespaced of all plants
- There are about 250.000 known species (including 720 gymnosperms)
- Often insects and othre animals transfer pollen of one flower to female sex organs on another flower
- Fruit develops from the carpel after fertilization - it helps dispersing seeds of Angiosperms; they are often carried by wind or aimals to new locations
- Angiosperms provide most of the food that sustain terrestrial life and they are source of many products used by humans
Flower is specialized for reproduction:
There are 4 types of modified leaves:
- Sepals (usually green)
- Petals (brightly coloured in most flowers)
- Stamens (produce stamene pollen)
- Carpels (Pistils) (produce ovules)

dąb - oak
klon - maple
jesion - ash
topola - poplar
lipa - linden
buk - beech
olcha - alder
brzoza - birch
wiąz - elm
grab - hornbeam
wierzba - willow
kasztanowiec - chestnut
diversed - zróżnicowane
angiosperms - okrytonasienne

1. General characteristics of plants
- They are autothropic
- They can photosynthesise
- They have got flowers and leaves
- Their cells contain chlorophyll
- They have roots
- They are eucaryotes - their cells have the nucleus
- Their cell wall is made of cellulose
- They have got vacuoles
samożywny - autothropic
eukarioty - eucaryotes
jądro - nucleus
wodniczka - vacuole
2. Plants' reproduction
- Plants have sex organs which prevent of desiccation (drying out) of developing gamets
- Sex organs prevent them by providing them with water and nutrients within a female reproductive structure
- Almost all of them reproduce sexually
- Have a life cycle that is alternation of generations
- Alternation of generations is a term used for describing the life cycle of plants; can exist in two forms: gametophyte and sporophyte
desiccation - wysychanie
developing (gamets) - rozwijające się (gamety)
alternation of generations - przemiana pokoleń
3. Non-vascular plants
- They are restricted to the bryophytes
- Only bryophytes haven't got the vascular tissue for water transport
- Bryophytes include liveworts and mosses
- They can be found in moist locations, because they haven't got roots, leaves and vascular tissue
Reproduction of bryophytes:
- In alternation of generations the gametophyte is dominant
- They need water for fertilization, because the sperm must swim in external moisture to reach the eggs (during sexual reproduction)
a gametophyte - a small, free-living organism that produce gamets (sperm and egg cells); they need water for fertilization
a sporophyte - produces many windblown spores, that disperse the species
rośliny naczyniowe - vascular plants
mszaki - bryophytes
tkanka przewodząca - vascular tissue
wątrobowce - liveworts
mchy - mosses
wilgotne (miejsca) - moist locations
rozprzestrzeniać - to disperse
zapłodnienie - fertilization
4. Primitive vascular plants
- Ferns are primitive vascular plants
- They have true leaves and roots
- They haven't got flowers and seeds, but they reproduce by
spores - Their life cycle (alternation of generations) is characterised by a dominant sporophyte; they produce spores
- Ferns vary in appearance; many of them are low-lying, but there are also tall-tree ferns in the tropics
- Ferns grow in moist and shady woodlands, deserts, rocks, open field, in water
- There are about 10.000 species known - including: whisk ferns, horse tails and club mosses
paprocie - ferns
nizinny - low-lying
zacieniony - shady
paprocie - whisk ferns
skrzypy - horse tails
widłaki - club mosses
korzenie przybyszowe - adventitious roots

5. Seed plants; gymnosperms
- They are vascular plants that produce seeds
- A seed consists of a plant embryo packed along with a food supply within a protective coat
- After a period of dormancy and when environmental factors are favourable (suitable temperature, water and oxygene), stored food will be mobilized and the seed will germinate
- A seed become an important means of dispersing offspring
- A pollen grain can be dispersed through the air or transported by animals - it doesn't need water for fertilizaton
- Seeds-bearing plants are the most succesful land plants, and they dominate the Earth's land-base vegetation
Gymnosperms
- They are group of seed plants with ovules on scales, which are usually arranged in cone-like structures
- Most of them are evergreen (retain leaves throughout the year)
- The needle-shaped leaves are adapted to dry conditions
- Coniferous trees are the oldest and the largest organisms on Earth
nagonasienne - gymnosperms
kiełkować - to germinate
w kształcie igły - needle-shaped
łuska (zalążki na łuskach - scale (ovules on scale)
wiecznie zielone - evergreen
pylnik - anther
pręcik - stamen
nitka pręcika - filament
płatki korony - petals
działki kielicha - sepals
znamię słupka - stigma
szyjka - stile
słupek - carpel
zalążek - ovule
zalążnia - ovary

sosna - pine
świerk - spruce
kosodrzewina - dwarf
limba - swiss pine
jodła - fir
cis - yew
jałowiec - juniper
modrzew - larch
6. Seed plants; angiosperms
- Angiosperms (flowering plants) are vascular seed plants that produce flower and fruits as reproductive structures
- They are most diversed and geographically widespaced of all plants
- There are about 250.000 known species (including 720 gymnosperms)
- Often insects and othre animals transfer pollen of one flower to female sex organs on another flower
- Fruit develops from the carpel after fertilization - it helps dispersing seeds of Angiosperms; they are often carried by wind or aimals to new locations
- Angiosperms provide most of the food that sustain terrestrial life and they are source of many products used by humans
Flower is specialized for reproduction:
There are 4 types of modified leaves:
- Sepals (usually green)
- Petals (brightly coloured in most flowers)
- Stamens (produce stamene pollen)
- Carpels (Pistils) (produce ovules)

dąb - oak
klon - maple
jesion - ash
topola - poplar
lipa - linden
buk - beech
olcha - alder
brzoza - birch
wiąz - elm
grab - hornbeam
wierzba - willow
kasztanowiec - chestnut
diversed - zróżnicowane
angiosperms - okrytonasienne

©2011-2013 by Oskar Zmarzły
